The Art of RAW Conversion #001
"RAW Converter
Essentials"

note by
Uwe Steinmueller
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
Over the next coming months we will have a look at some more new and
updated RAW converters (PhaseOne CaptureOne, Nikon Capture 3.5, Kodak
Photo Desk 3.0, ...).
We want to have a framework how to judge the quality of the diverse
RAW converters. That we want to summarize what a RAW converter needs
to do.
- Some features are essential and need to be supported by the RAW
converter
- Other features can also be done later in Photoshop or some plug-in
- Finally there are some functional requirements a RAW converter has
to meet to be useful
|
| The RAW Workflow |
| |
| Here is a diagram of the whole principle RAW file workflow: |
| |

Principle Workflow Steps |
| |
| The rest of this article will discuss which of these
steps are the responsibilty of a RAW converte.r |
| |
| |
| RAW Converter Responsibilities |
| |
| This section lists the responsibilities and we later
discuss them in some detail |
| |
| Responsibility |
Where required? |
| |
|
| Bayer
Pattern interpolation |
Converter |
| |
|
| Apply Tone Curve |
Converter (*) |
| |
|
| Apply Camera Profile |
Converter (*) |
| |
|
| White Balance (WB) |
Converter |
| |
|
| Exposure Compensation (EV) |
Converter |
| |
|
| Rotate 90 (CW,CCW) and 180 degrees |
Converter, Browser, Photoshop |
| |
|
| Noise removal |
Converter of Photoshop |
| |
|
| Artifact Removal (e.g. noise) |
Converter or Photoshop |
| |
|
| Contrast and Brightness (Levels, Curves) |
Converter or Photoshop |
| |
|
| Saturation |
Converter or Photoshop |
| |
|
| Sharpening |
Converter or Photoshop |
| |
|
| Color Corrections |
Converter or Photoshop |
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
| (*) Can be done in Photoshop if the so called linear
conversion is used (see later) |
| |
| RAW converter Features |
| |
- User interface experience
- Support for Color Management (Monitor profile, Camera profiles,
Output Profiles)
- Histogram or equivalent aid for EV correction
- Reasonable large preview
- Realtime WB, EV and other correction preview
- Batch capabilities
- Good workflow integration
- Integration with RAW image browser
- Saving and recalling settings or setting groups (like WB, Sharpening,
...)
- Saving files at 16bit
- Tag saved files with profiles
- Record RAW conversion settings
|
| |
|
There are actually two extreme schools of RAW conversion strategies
and all RAW converters fall somewhere in between:
- Linear conversion: Performs only the interpolation,
EV and WB in the RAW converter and the rest in Photoshop using actions,
plug-ins or automation.
- Full Service Conversion: Does all the jobs in the
RAW converter. Photoshop is only used for final retouching (dust removal,
minor corrections)
|
| |
| Linear Conversion |
| |
| As said the linear conversion only performs the RAW
interpolation (for more detail read
here), EV and WB. The result is a dangerously dark image. |
| |

Linear converted file
|
| |
| This looks to us like a very bad exposed file. This
is not the case as all(!) interpolated RAW files look like this if only
the interpolation had been done. To get this image to life a so called
"tone curve" is applied. |
| |
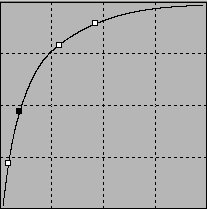
Tone Curve
|
| |
| Also this is not really the kind of curve one would
use every day. In most cases this tone curve is actually part of a generic
camera profile. |
| |

Resulting image after profile and tone curve have been applied
|
| |
| RAW Converter Essentials |
| |
| Interpolation |
| |
|
This is the key responsibility of the RAW converter. There are many
differences in the quality of RAW interpolation:
- How many details are resolved (especially in the shadows)?
- Does the noise get amplified by pulling out too much detail?
- Stair casing in fine lines?
If readers know more criteria it would be very helpful to send me their
feedback.
|
| |
| Tone Curve and Camera Profiles |
| |
| A RAW converter should come with good generic camera
profiles for all cameras supported |
| |
| White Balance (WB) |
| |
|
Good white balance support is crucial for any useful RAW converter.
It should be clear that WB correction without support for monitor profiles
does not make too much sense. There are two kinds of WB correction techniques:
- Gray balance by clicking on a neutral spot in the photo
- WB correction controls (mostly in terms of presets and/or color
temperature)
Good white balance support is not a trivial task for any RAW converter.
|
| |
| Exposure (EV) |
| |
| Also good exposure compensation is essential. The tools
should be aided by a histogram or equivalent (under- and overexposure)
indicators. |
| |
| Noise Removal (NR) |
| |
|
Generally it is a good idea to remove the noise as early as possible
before it gets amplified in the next steps. Also the noise removal routine
can make use of metadata like ISO and camera model.We pretty sure that
we will see also some improvements on noise removal over the next months
(Currently the best noise removal tools seem to exist as external tools
- especially NeatImage gets high marks - or Photoshop plug-ins, Nik
Multimedia announced a tool called Dfine).
Noise removal normally also lowers the sharpness of the image and that
is why NR and sharpening are very much correlated.
|
| |
| Artifact Removal (Moire) |
| |
|
Sometimes noise and artifacts are treated as the same. Here is our
view:
- Noise is a result of the image capturing process especially in the
shadows
- Artifacts are the result of the Bayer pattern limitations and the
interpolation process
Moire removal is especially important for cameras with a weak AA (Anti
Aliasing) filter (e.g. Fuji S2, Canon 1D, Kodak 760 without AA filter).
Removing moire can be nasty or even impossible sometimes.
|
| |
| Contrast, Brightness, Saturation, Color Corrections
and Sharpening |
| |
| These steps are usually bet done in Photoshop. But if
the RAW converter delivers these tools in a good quality then this can
speed up the RAW file workflow significantly. |
| |
| We hope you find this summary helpful and we now have
a framework for all our future reviews on new and updated RAW converters. |
| |
| |
| |
| |
|
|
| |
| |